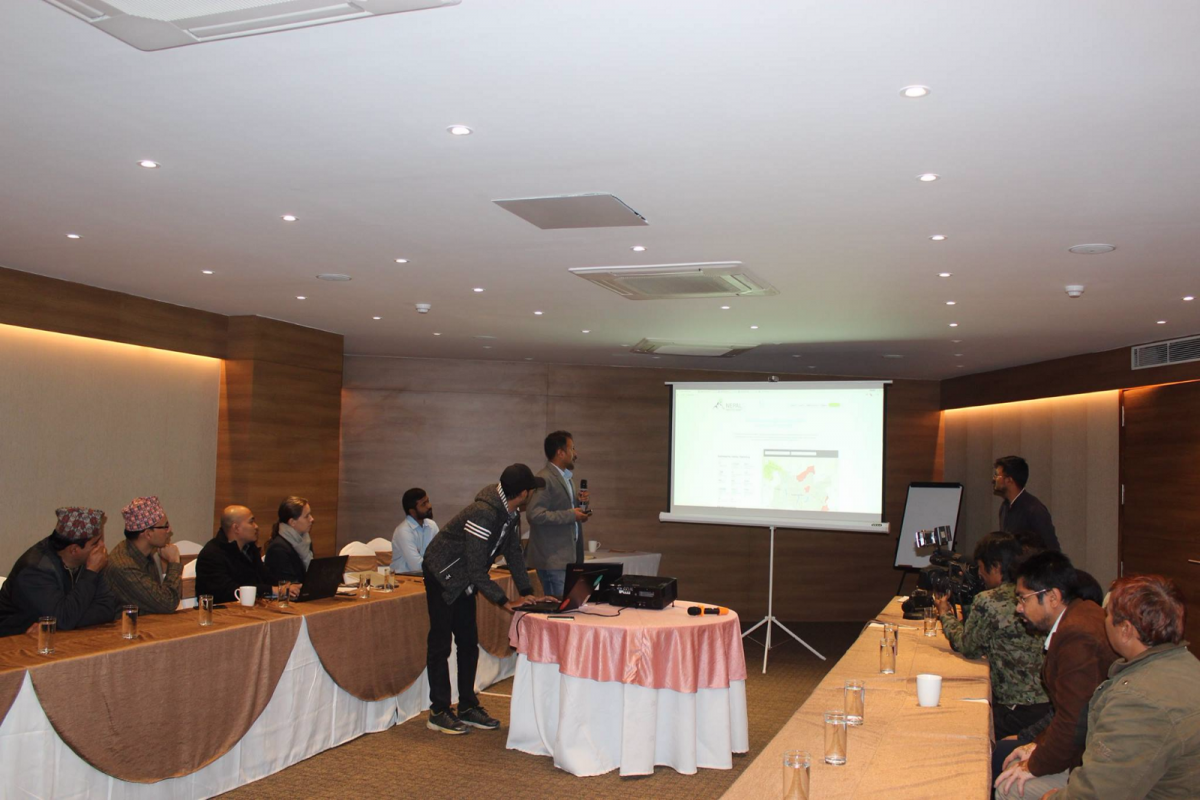
This post was first published on YoungInnovations blog as Use of data & technology for promoting waste sector accountability in Nepal. YoungInnovations is a technology company that creates innovative and powerful solutions to global development problems.
All the Nepalese people are saddened to see waste abandoned in the Capital, Kathmandu. Among them, many are concerned to find solutions to such a problem, including Kathmandu City. A 2015 report stated that Kathmandu Metropolitan City (KMC) alone receives 525 tonnes of waste in a day while it manages to collect 516 tonnes out if it, meaning that 8 tonnes of waste are left/abandoned. Many suspect that this is not true as the Metropolitan City’s record keeping system might not be properly maintained. However, 8 tonnes of abandoned solid waste a day is enough to make the city untidy, contaminate water sources, plastic burning as well as other associated problems.
Technology for waste sector accountability
Despite many stakeholders including the government sector, non-governmental organizations, private sectors have been working to address the problem associated with solid waste mapping in urban sector, the problem continued to exist.
YoungInnovations and Clean Up Nepal came together to discuss if we could tackle this problem. We discussed if keeping track of everybody’s efforts as well as noticing every piece of waste in the city raises accountability of stakeholders adds a value. YoungInnovations has over a decade of experience in developing data and evidence-based tech solutions to problem. Clean Up Nepal is a civil society organization working to provide an enabling environment to improve solid waste management and water, sanitation and hygiene in Nepal by working closely with local communities and relevant stakeholders. In this, both the organizations agreed to work mixing the expertise of each other to offer the government with an technology that avails stakeholders with proper data related to solid waste and its management.
Also, the preliminary idea was tested with some ongoing initiatives of such kind (Waste Atlas, Letsdoitworld etc) while consultations were held with some of the organizations like The GovLab, ICIMOD learn from their expertise on open data as well as environmental aspects. A remarkable example of smart waste management being carried out in Ulaanbaatar, Capital of Mongolia did motivate us to test the idea in Nepal.
After several pitching, the idea was able to secure financial support from the Department for International Development (DFID) as well as collaborative support from Development Initiatives and The Asia Foundation.
No data ? Started collecting !
When we started building the idea, there was no data related to solid waste that we could test and refine the idea.
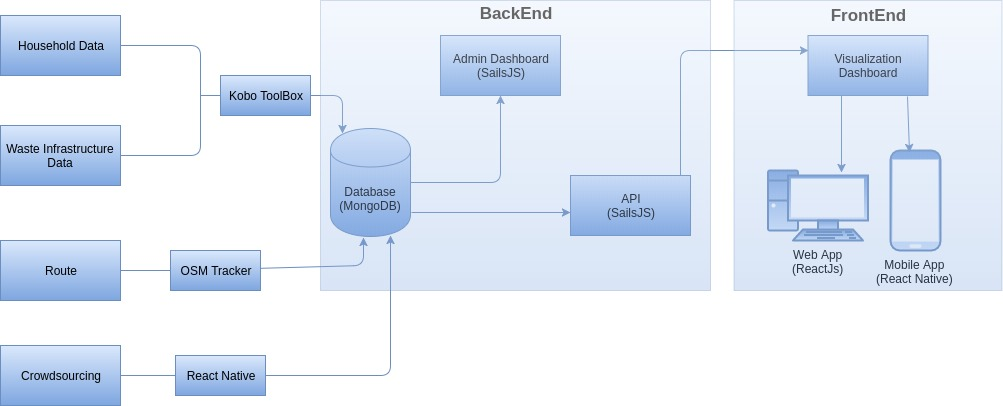
Instead of waiting, we started collecting primary data. We developed android phone-based data collection tools with the use of KoBoToolbox and OSM Tracker, and we trained the volunteers to use the tool and received significant data under the following:
- Waste infrastructures (Waste bins, waste dumping spots, scrap dealers, transfer stations, composting centers, landfill sites)
- Household coverage of the waste services (house category, subscription to the waste collection companies, fees paid against services, fees paid, frequency of waste collection)
- Waste Companies profile (scope of service, capacity as well as waste collection schedule)
- Waste Collection routes (GPS routes along with the timing and key actions)
- Illegal waste dumping and burning spots (as a test for crowdsourcing)
Provided there were limitations for us to carry out the project within limited time as well as resources, only three wards out of 35 wards in Kathmandu Metropolitan City were chosen to establish the proof of concept.
Technology Development
Collection of data helped us to see the existing scenario and to develop appropriate technological platforms to fulfil the project objective.
With a number of testings and consultations, we were able to come up with the mobile and web based applications
Nepal Waste Map Web App
Nepal Waste Map web is a composite of several features primarily focused at the following:
- Display of key stats and information about solid waste
- Admin panel to interact with the data for taking possible actions (update, edit and delete)
Key Features of Nepal Waste Map Web
Following are the key feature of the App:
- Waste Map of the KMC’s three wards with data related to waste infrastructure, household coverage of waste services, waste collection companies, waste collection routes available in real time.
- Resources as learning materials
- Admin Panel for super admin to create admins depending upon their natures (government, private company etc) allowing to see the quality of data, edit upon needed as well as take action
- Engaging option for government, private sectors, local governments or others with various programs and events with Clean Up Nepal.
Nepal Waste Map Mobile
A Mobile App primarily reflects Nepal Waste Map in the mobile phones. Most of the features resemble with the Nepal Waste Map Web App.
However, some functionalities in the app are key in terms of data aspects:
Crowdsourcing Functionality
Any public (users) who use the app can report issues related to illegal waste dumping and waste esp. Plastic burning. Example: if I saw somebody burning plastic wastes, I can use the app for reporting such an incident along with the photo as evidence as well as coordinates. The admin of the web app can view the report in a real time and take action (not limited to defined as acknowledge and marking resolved).
Data Collection
The App is peculiar as it itself serves as a tool to input new data. The admin of the Nepal Waste Map can themselves supply with new primary data. The admins have an access to following collection forms together with coordinates and photos:
- Waste infrastructures (Waste bins/containers, waste dumping spots, scrap dealers, transfer stations, composting centers, landfill sites)
- Household coverage of the waste services (house category, subscription to the waste collection companies, fees paid against services, fees paid, frequency of waste collection)
- Waste Companies profile (scope of service, capacity as well as waste collection schedule)
- Waste Collection routes (GPS routes along with the timing and key actions
Key Technologies Adopted
YoungInnovations has acknowledged Nepal Waste Map as an innovative idea through its blog while listing out its achievements in the year 2017. We adopted various technologies to develop Nepal Waste Map to meet the needs and demands of various stakeholders.
Technology Overview
We used ReactJS as the frontend technology for this project. For the web application we used Sails.js, a Node.js framework for the backend technology. As the data are huge and functionality needs to be smooth we decided using Node.js. We used MongoDB, a non-relational database to store the data for the application. The KoboToolbox, a data collection tool that we employed to collect the data, also stores the data in MongoDB. We import the data from KoboToolbox to our system before the data is reflected in the application. We need to process and clean the data collected from the KoboToolbox, so it makes sense to setup a new database for our application, rather than using the database used by KoboToolbox.
Data Collection
KoBoToolbox
KoBoToolbox is a free open-source tool for collecting data through the use of mobile (android) phones. It can be used offline while collecting data once the deployed form is downloaded.
OSM tracker
OSMTracker is an offline GPS tracker mobile app for android designed for collecting points of interest (POI) to be added to the map and for recording GPX tracks. OSMTracker data is exported in GPX format with waypoints, making it suitable for import into the JOSM map editor. One can also thus directly upload waypoints when one uploads tracks. OSMTracker is also highly customizable.
Backend
Admin Panel Development
For developing the Admin Panel of the Web, we used SailsJs for constructing API and admin dashboard. All the waste mapping data in mobile and web app are accessed through these APIs. The issues reported from the mobile can be accessed through the admin panel for further acknowledgement. All the waste mapping data can be customized through the admin panel.
Frontend
UI design
We used Figma as UI/UX design tool for this project. And we tried zeplin as collaboration tool on design and project requirements among developers, designers and stakeholders. Zeplin helped us to share our designs quickly to our stakeholders and get feedbacks on time.
We implemented reactjs as UI library for the web portal.
Mapping Technologies
In this project, we used Leafletjs open source javascript library to show a lot geographical data in map. To make map more interactive and user friendly we used few leaflet plugins such as LeafletBasemap, fullscreen, loading control etc.
We took training to volunteers of cleanup nepal on how to use OSM tracker android app to get route data. Volunteers went to field with waste collector team to collect route data and provide us data. OSM tracker android app gives us data in gpx format which we then refined as we needed using JSOM software. JSOM is a free software desktop editing tool for OpenStreetMap geodata.
Mobile Application
We used React Native for the mobile platform. Since we are using ReactJS, we could use web app logic on the React Native based mobile platform as well. For the map, we used google map package built by AirBnb instead of leaflet js used on the web, as the google map api is free to use for the mobile application. For the UI component library, we used NativeBase. This UI library makes it easier to build native UI component for both iOS and android platforms. For camera feature, we used reactive-camera package and for gallery we have have created our own custom gallery component. Some of the key components used in mobile application are as follows:
- React native maps : Airbnb’s React Native Mapview component for iOS & Android
- React native camera : Camera component for react-native
- React native fbsdk : A React Native wrapper around the Facebook SDKs for Android & iOS
- React native geocoder : Geocoding services for react native
- Native Base : Cross platform UI for react-native
Conclusion
Since technology is just a means to an end, the utilization of the tech platforms by the concerned stakeholders always determine the sustainability of the idea. We believe that the platforms/tools are more subject to use and revise to adapt with the changing scenario.
Similar to the Tools and Technologies of Nepal Waste Map, it has a potential to expand its coverage upon understood that the data and technology driven innovations are more usable if properly defined and utilized.
* The blog is prepared together with inputs from Biju Nakarmi, Saurabh Sharma, Suraj K.C, Bimal Gurung and Bijay Basnet (the YI team behind the development of the platform)
-
Apple iPad 2025 Arrives in Nepal with A16 BionicHIGHLIGHTS The Apple iPad 2025 price in Nepal starts from Rs. 65,000 (128GB). It is…
-
Xiaomi Pad 7 Launching in Nepal Soon: Best iPad Alternative?HIGHLIGHTS Xiaomi Pad 7 price in Nepal could be Rs. 44,999 (8/128GB) and Rs. 49,999…
-
Honor X8c with 120Hz Display Launched in Nepal with an Early Bird OfferHIGHLIGHTS Honor X8c price in Nepal is Rs. 33,999 (8/512GB). It is powered by the…